How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to advanced applications in various industries. Mastering drone operation requires understanding not only the mechanics of flight but also crucial safety protocols, legal considerations, and the art of capturing stunning visuals. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and creatively.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checklists and essential safety procedures to navigating different flight modes and planning effective missions. Learn how to capture professional-quality aerial photos and videos, troubleshoot common issues, and stay compliant with all relevant regulations. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will serve as your ultimate resource for safe and successful drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures optimal performance. Overlooking even minor steps can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, perform a thorough inspection. This includes verifying battery charge levels (ideally above 80% for optimal flight time and safety), visually inspecting propellers for damage or wear, and ensuring all components are securely fastened. Confirm GPS signal acquisition; a strong signal is essential for accurate positioning and stable flight. Check the drone’s overall condition, noting any loose parts or unusual wear.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. These guidelines protect both the drone and its surroundings.
| Regulation Category | Specific Regulation | Best Practice | Consequences of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airspace Restrictions | Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace. | Always check airspace regulations using apps like B4UFLY or AirMap before each flight. | Fines, legal action, and potential accidents. |
| Visual Line of Sight | Maintain visual contact with your drone at all times. | Avoid flying beyond your visual range. Use a spotter if necessary in challenging environments. | Loss of control and potential damage. |
| Weather Conditions | Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds, rain, or fog. | Check weather forecasts before each flight and postpone if conditions are unfavorable. | Loss of control, damage to the drone, and potential injury. |
| Privacy and Data Protection | Respect people’s privacy and avoid capturing images or videos without consent. | Be mindful of where you are flying and who you might be recording. | Legal repercussions and reputational damage. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is fundamental for safe and efficient operation. Different drones may have slightly varying controls, but the basic principles remain consistent.
Drone Controls
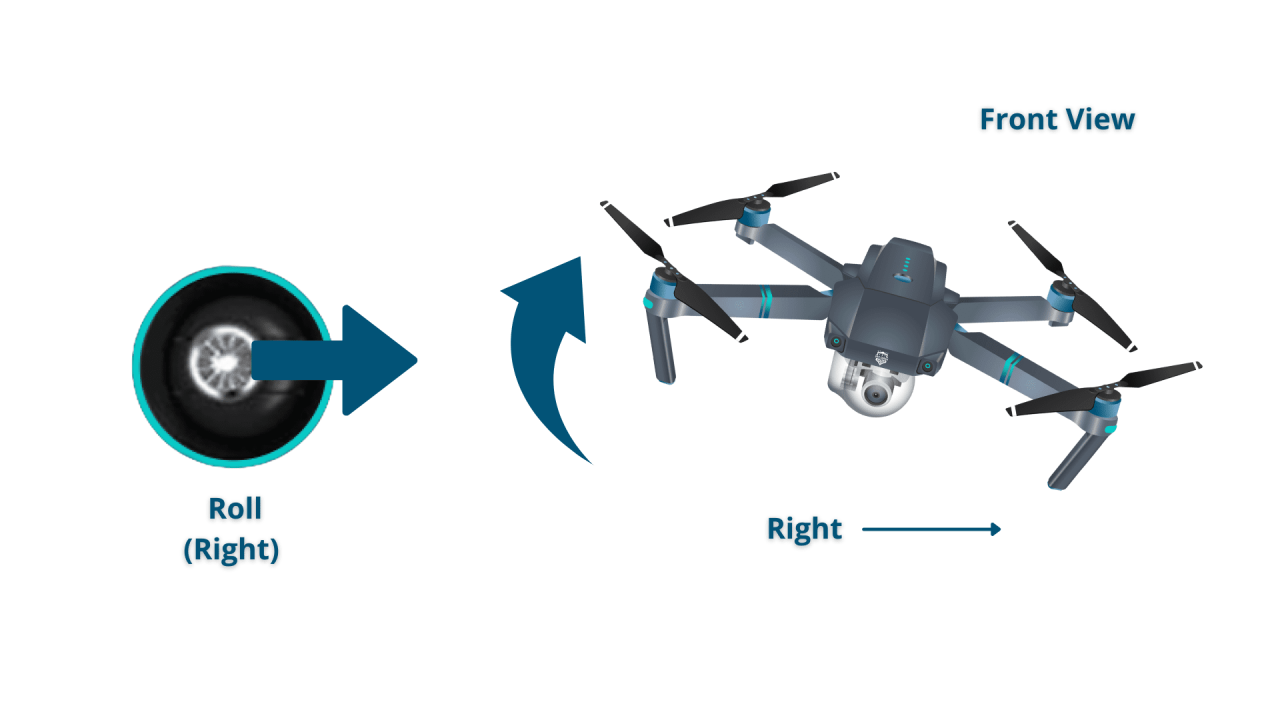
Typical drone controls include throttle (controls altitude), yaw (rotates the drone left or right), pitch (tilts the drone forward or backward), and roll (tilts the drone left or right). These controls work in conjunction to maneuver the drone in three-dimensional space. Many drones offer adjustable control sensitivity, allowing pilots to customize their experience.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, making it ideal for new pilots. Sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers and higher speeds, while GPS mode utilizes satellite data for precise positioning and stability, particularly useful for long-range flights.
Navigation Methods
Drones navigate using various methods. GPS utilizes satellite signals for precise location and navigation. Visual positioning relies on cameras and computer vision to track the drone’s position relative to its surroundings. Manual control allows for direct manipulation of the drone using the controller’s sticks. Each method has strengths and weaknesses, with GPS being generally more reliable for long-range and autonomous flights, while visual positioning is crucial for indoor or GPS-denied environments.
Safe Takeoff and Landing
A safe and controlled takeoff and landing are crucial for preventing accidents. Begin by ensuring the drone has a strong GPS signal and is properly calibrated. Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically. For landing, slowly reduce the throttle, maintaining a controlled descent. Avoid abrupt movements.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Flight planning is essential for a successful and safe drone mission. Careful planning minimizes risks and maximizes the efficiency of the flight. Failing to plan can lead to accidents or missed opportunities.
Flight Path Planning
Before each flight, plan the drone’s path, considering obstacles, airspace restrictions, and the desired shots. Simple flights may involve straight lines, while more complex missions might include circular patterns or waypoint navigation. Waypoints allow the drone to follow a pre-programmed route autonomously.
Obstacle Avoidance
Many modern drones offer obstacle avoidance systems using sensors to detect and avoid obstacles. However, even with these systems, it is crucial to maintain visual awareness and plan a flight path that minimizes potential collisions. Keeping a safe distance from obstacles is always a good practice.
Drone Mission Flowchart
A flowchart visually represents the steps involved in planning and executing a drone mission. It starts with pre-flight checks, proceeds to flight path planning, incorporates the flight itself, includes data acquisition, and concludes with post-flight procedures and data analysis. This structured approach ensures all steps are accounted for.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively handle your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you can confidently take to the skies.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
High-quality aerial photography and videography require understanding camera settings and employing effective techniques. Mastering these skills significantly enhances the final product.
Camera Settings and Image Quality

Camera settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, directly impact image quality. A higher ISO increases sensitivity to light but can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur, while aperture controls depth of field. Understanding how these settings interact is key to capturing sharp, well-exposed images.
Capturing High-Quality Footage
Techniques like proper framing, composition (using the rule of thirds, leading lines, etc.), and good lighting are essential for professional-looking aerial shots. Consider the time of day for optimal lighting conditions, and use the drone’s gimbal to stabilize the camera and prevent unwanted shaking.
Using Drone Features
Features such as the gimbal (for smooth, stabilized footage) and zoom (for close-up shots) enhance image capture. Experiment with these features to find the best settings for different scenarios.
Tips for Professional Aerial Footage
- Plan your shots carefully, considering composition and lighting.
- Use the gimbal to stabilize your footage.
- Experiment with different camera settings to achieve the desired look.
- Practice smooth, controlled movements.
- Edit your footage to remove any unwanted sections.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their solutions is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Quick diagnosis and appropriate action minimize downtime and prevent further damage.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Low battery is a common issue, requiring immediate landing and battery replacement or charging. GPS signal loss can be addressed by moving to an area with better reception or restarting the drone. Motor failure may require professional repair or replacement. Each issue demands specific troubleshooting steps.
Preventative Measures
Regular maintenance, proper storage, and avoiding extreme conditions significantly reduce the risk of malfunctions. Keeping the drone clean and dry is essential, as is regularly checking battery health and propellers for damage.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Excessive flight time, low battery charge | Land immediately, replace or charge battery |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, weak signal | Relocate to open area with strong signal, restart drone |
| Motor Failure | Physical damage, wear and tear | Inspect motor, replace if necessary (may require professional assistance) |
| Propeller Damage | Collision, wear and tear | Replace damaged propeller |
Drone Maintenance and Storage

Proper maintenance and storage significantly extend the lifespan of a drone. Neglecting these aspects can lead to premature wear and tear and costly repairs.
Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures
Regularly clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens using a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solutions. Inspect for loose parts, damage, or wear. Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer.
Essential Tools and Materials
Basic tools include a soft cloth, lens cleaning solution, compressed air, and a small brush. Specialized tools might be needed for more complex maintenance tasks.
Proper Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep the battery charged to a moderate level (around 50%) to prevent damage from overcharging or deep discharge.
Replacing Damaged Parts
Replacing damaged parts often requires specific tools and knowledge. Consult the drone’s manual or seek professional assistance if unsure about the repair process.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires adherence to local, national, and international laws and regulations. Ignorance of these regulations can lead to serious consequences.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations governing drone operation in your area. These regulations vary by country and region.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on the drone’s capabilities and intended use, obtaining necessary permits and licenses might be required. These permits usually cover commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Always check for airspace restrictions and no-fly zones before each flight. These areas are often near airports, military bases, or other sensitive locations.
Best Practices for Compliance
Maintain detailed flight logs, respect privacy, and always operate your drone responsibly and within legal limits. Regularly update yourself on changes in regulations.
Advanced Drone Features and Applications
Modern drones offer advanced features and a wide range of applications beyond basic photography and videography. Understanding these features expands the possibilities for drone use.
Advanced Drone Features
Obstacle avoidance systems use sensors to automatically avoid collisions. Follow-me mode allows the drone to track a subject autonomously. Point of interest allows the drone to orbit a specific location.
Drone Applications
Drones are used in various sectors including photography, videography, infrastructure inspection, delivery services, search and rescue, and agriculture. Their versatility continues to expand.
Drone Types and Capabilities, How to operate a drone
Different drone types offer varying capabilities. Some are designed for photography, others for heavy lifting, and some are specialized for specific tasks.
Autonomous Flight Programming
Some drones allow for autonomous flight programming using software and specialized controllers. This enables complex flight maneuvers and automated data acquisition.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a keen eye for detail. From meticulous pre-flight checks to understanding airspace restrictions and mastering flight controls, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding experience. By adhering to best practices and continuously honing your skills, you can unlock the full potential of your drone, capturing stunning visuals and exploring the limitless possibilities of aerial technology.
Remember, responsible drone operation not only ensures your safety but also protects the environment and the airspace shared by others.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial step is learning the basics of controlling the drone itself, and for comprehensive guidance, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. This will cover everything from takeoff and landing procedures to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re prepared to safely and effectively operate your drone.
User Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes on a single charge, often less in windy conditions.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have return-to-home (RTH) functionality. However, maintaining visual contact and practicing safe flying habits is crucial. Consider flying in areas with good GPS reception.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, particularly for more expensive models or commercial use. It protects you against accidents and potential liability.